< C++ .NET and Using ADO.NET 3 | Main | C++ .NET and Using ADO.NET 5 >
C++ .NET And Using ADO.NET 4
What we have in this page?
-
DataSet Class
-
DataSet Members
-
Creating the Form
DataSet Class
The DataSet, which is an in-memory cache of data retrieved from a data source, is a major component of the ADO.NET architecture. The DataSet consists of a collection of DataTable objects that you can relate to each other with DataRelation objects. You can also enforce data integrity in the DataSet by using the UniqueConstraint and ForeignKeyConstraint objects. Whereas DataTable objects contain the data, the DataRelationCollection allows you to navigate though the table hierarchy. The tables are contained in a DataTableCollection accessed through the Tables property. When accessing DataTable objects, note that they are conditionally case sensitive. For example, if one DataTable is named "mydatatable" and another is named "Mydatatable", a string used to search for one of the tables is regarded as case sensitive. However, if "mydatatable" exists and "Mydatatable" does not, the search string is regarded as case insensitive. A DataSet can read and write data and schema as XML documents. The data and schema can then be transported across HTTP and used by any application, on any platform that is XML-enabled. You can save the schema as an XML schema with the WriteXmlSchema method, and both schema and data can be saved using the WriteXml method. To read an XML document that includes both schema and data, use the ReadXml method. In a typical multiple-tier implementation, the steps for creating and refreshing a DataSet, and in turn, updating the original data are to:
The DataSet and DataTable objects inherit from MarshalByValueComponent, and support the ISerializable interface for remoting. These are the only ADO.NET objects that can be remoted. The ADO.NET DataSet is a memory-resident representation of data that provides a consistent relational programming model regardless of the source of the data it contains. A DataSet represents a complete set of data including the tables that contain, order, and constrain the data, as well as the relationships between the tables. There are several ways of working with a DataSet, which can be applied independently or in combination. You can:
|
A strongly typed DataSet can also be transported using an XML Web service. The design of the DataSet makes it ideal for transporting data using XML Web services.
DataSet Members
The following tables list the members exposed by the DataSet type.
| Public Constructors | |
| Name | Description |
| Symbol | |
| DataSet | Overloaded. Initializes a new instance of the DataSet class. |
|
Table 9 | |
| Protected Constructors | |
| Name | Description |
| Symbol | |
| DataSet | Overloaded. Initializes a new instance of the DataSet class. |
|
Table 10 | |
| Public Properties | |
| Name | Description |
| Symbol | |
| CaseSensitive | Gets or sets a value indicating whether string comparisons within DataTable objects are case-sensitive. |
| Container | Gets the container for the component. (Inherited from MarshalByValueComponent.) |
| DataSetName | Gets or sets the name of the current DataSet. |
| DefaultViewManager | Gets a custom view of the data contained in the DataSet to allow filtering, searching, and navigating using a custom DataViewManager. |
| DesignMode | Gets a value indicating whether the component is currently in design mode. Inherited from MarshalByValueComponent.) |
| EnforceConstraints | Gets or sets a value indicating whether constraint rules are followed when attempting any update operation. |
| ExtendedProperties | Gets the collection of customized user information associated with the DataSet. |
| HasErrors | Gets a value indicating whether there are errors in any of the DataTable objects within this DataSet. |
| IsInitialized | Gets a value that indicates whether the DataSet is initialized. |
| Locale | Gets or sets the locale information used to compare strings within the table. |
| Namespace | Gets or sets the namespace of the DataSet. |
| Prefix | Gets or sets an XML prefix that aliases the namespace of the DataSet. |
| Relations | Get the collection of relations that link tables and allow navigation from parent tables to child tables. |
| RemotingFormat | Gets or sets a SerializationFormat for the DataSet used during remoting. |
| SchemaSerializationMode | Gets or sets a SchemaSerializationMode for a DataSet. |
| Site | Overridden. Gets or sets a System.ComponentModel.ISite for the DataSet. |
| Tables | Gets the collection of tables contained in the DataSet. |
|
Table 11 | |
| Protected Properties | |
| Name | Description |
| Symbol | |
| Events | Gets the list of event handlers that are attached to this component. (Inherited from MarshalByValueComponent.) |
|
Table 12 | |
| Public Methods | |
| Name | Description |
| Symbol | |
| AcceptChanges | Commits all the changes made to this DataSet since it was loaded or since the last time AcceptChanges was called. |
| BeginInit | Begins the initialization of a DataSet that is used on a form or used by another component. The initialization occurs at run-time. |
| Clear | Clears the DataSet of any data by removing all rows in all tables. |
| Clone | Copies the structure of the DataSet, including all DataTable schemas, relations, and constraints. Does not copy any data. |
| Copy | Copies both the structure and data for this DataSet. |
| CreateDataReader | Overloaded. Returns a DataTableReader with one result set per DataTable, in the same sequence as the tables appear in the Tables collection. |
| Dispose | Overloaded. Releases the resources used by the MarshalByValueComponent. (Inherited from MarshalByValueComponent.) |
| EndInit | Ends the initialization of a DataSet that is used on a form or used by another component. The initialization occurs at run time. |
| Equals | Overloaded. Determines whether two Object instances are equal. (Inherited from Object.) |
| GetChanges | Overloaded. Gets a copy of the DataSet containing all changes made to it since it was last loaded, or since AcceptChanges was called. |
| GetDataSetSchema | - |
| GetHashCode | Serves as a hash function for a particular type. GetHashCode is suitable for use in hashing algorithms and data structures like a hash table. (Inherited from Object.) |
| GetObjectData | Populates a serialization information object with the data needed to serialize the DataSet. |
| GetService | Gets the implementer of the IServiceProvider. (Inherited from MarshalByValueComponent.) |
| GetType | Gets the Type of the current instance. (Inherited from Object.) |
| GetXml | Returns the XML representation of the data stored in the DataSet. |
| GetXmlSchema | Returns the XML Schema for the XML representation of the data stored in the DataSet. |
| HasChanges | Overloaded. Gets a value indicating whether the DataSet has changes, including new, deleted, or modified rows. |
| InferXmlSchema | Overloaded. Applies XML schema to the DataSet. |
| Load | Overloaded. Fills a DataSet with values from a data source using the supplied IDataReader. |
| Merge | Overloaded. Merges a specified DataSet, DataTable, or array of DataRow objects into the current DataSet or DataTable. |
| ReadXml | Overloaded. Reads XML schema and data into the DataSet. |
| ReadXmlSchema | Overloaded. Reads an XML schema into the DataSet. |
| ReferenceEquals | Determines whether the specified Object instances are the same instance. (Inherited from Object.) |
| RejectChanges | Rolls back all the changes made to the DataSet since it was created, or since the last time DataSet.AcceptChanges was called. |
| Reset | Resets the DataSet to its original state. Subclasses should override Reset to restore a DataSet to its original state. |
| ToString | Returns a String containing the name of the Component, if any. This method should not be overridden. (Inherited from MarshalByValueComponent.) |
| WriteXml | Overloaded. Writes XML data, and optionally the schema, from the DataSet. |
| WriteXmlSchema | Overloaded. Writes the DataSet structure as an XML schema. |
|
Table 13 | |
| Protected Methods | |
| Name | Description |
| Symbol | |
| DetermineSchemaSerializationMode | Overloaded. Determines the SchemaSerializationMode for a DataSet. |
| Dispose | Overloaded. Releases the resources used by the MarshalByValueComponent. (Inherited from MarshalByValueComponent.) |
| Finalize | [To be supplied.] (Inherited from MarshalByValueComponent.) |
| GetSchemaSerializable | - |
| GetSerializationData | - |
| InitializeDerivedDataSet | - |
| IsBinarySerialized | - |
| MemberwiseClone | Creates a shallow copy of the current Object. (Inherited from Object.) |
| OnPropertyChanging | Raises the OnPropertyChanging event. |
| OnRemoveRelation | Occurs when a DataRelation object is removed from a DataTable. |
| OnRemoveTable | Occurs when a DataTable is removed from a DataSet. |
| RaisePropertyChanging | Sends a notification that the specified DataSet property is about to change. |
| ReadXmlSerializable |
|
| ShouldSerializeRelations | Gets a value indicating whether Relations property should be persisted. |
| ShouldSerializeTables | Gets a value indicating whether Tables property should be persisted. |
|
Table 14 | |
| Public Events | |
| Name | Description |
| Symbol | |
| Disposed | Adds an event handler to listen to the Disposed event on the component. Inherited from MarshalByValueComponent.) |
| Initialized | Occurs after the DataSet is initialized. |
| MergeFailed | Occurs when a target and source DataRow have the same primary key value, and EnforceConstraints is set to true. |
|
Table 15 | |
| Explicit Interface Implementations | |
| Name | Description |
| Symbol | |
| System.ComponentModel.IListSource.GetList | For a description of this member, see IListSource.GetList. |
| System.Runtime.Serialization.ISerializable.GetObjectData | - |
| System.Xml.Serialization.IXmlSerializable.GetSchema | For a description of this member, see IXmlSerializable.GetSchema. |
| System.Xml.Serialization.IXmlSerializable.ReadXml | For a description of this member, see System.Xml.Serialization.IXmlSerializable.ReadXml. |
| System.Xml.Serialization.IXmlSerializable.WriteXml | For a description of this member, see System.Xml.Serialization.IXmlSerializable.WriteXml. |
| System.ComponentModel.IListSource.ContainsListCollection | For a description of this member, see System.ComponentModel.IListSource.ContainsListCollection. |
|
Table 16 | |
To illustrate these capabilities, you will create a new Windows Form application that will perform some of the previously discussed items.
Creating the Form
In this exercise, you will create a new application to perform some of the operations described in the previous section. The first step is to create the form.
1. Create a Visual C++ CLR Windows Forms Application project named DisconnectedApplication.

2. Open Solution Explorer, and look at the Source Files folder. Right-click Form1.h and select View Code from the context menu to view it in the code editor. Or select a form designer, right-click and select View Code context menu.
3. Add the following using directive to the end of the list:
// OleDb data provider definitions
using namespace System::Data::OleDb;

4. Back to the form designer. Set the Text for the form to Products. Add a DataGridView to the form, giving it the Name dgProducts. Size the DataGrid to fill most of the form.
5. Build your program, and fix any compiler errors. Run the program. If all is well, a form should appear as shown in the following figure.
| |
6. At the bottom of the designer, if you have noticed, the BindingSource and TableAdapter controls already added to the project when we add DataGridView control. This make our tasks easier compared to the previous version, the DataGrid control. Back to the designer, open the DataGridView Tasks and tick all the tick boxes. Select the Choose Data Source menu.

7. We are going to add the Northwind.mdb data source to our DataGtridView control. Select Add Project Data Source menu.

8. In Data Source Configuration Wizard dialog box, select Database icon and click the Next button.

9. Click the New Connection… button to add the new data connection.
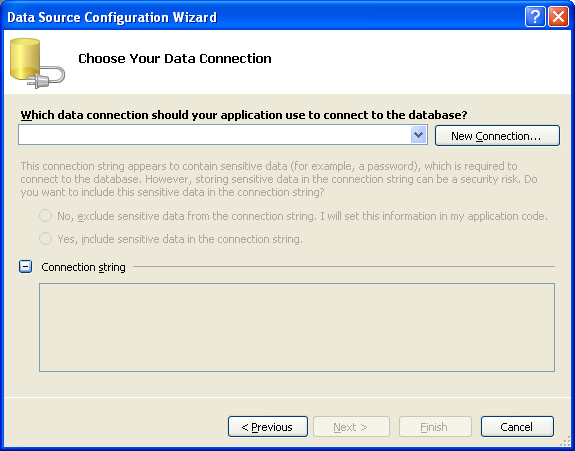
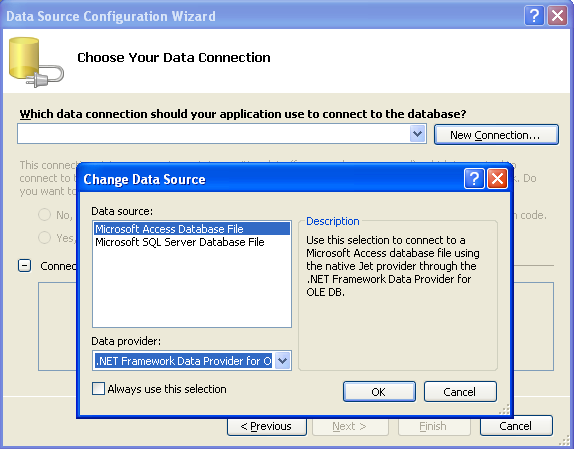
10. Next, select Microsoft Access Database File in the Change Data Source dialog box and click the OK button. Only .NET Framework Data Provider OLE DB (Microsoft Jet 4.0 OLE DB Provider) available for Microsoft Access.
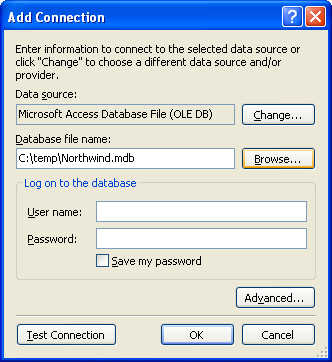
11. Click the Browse… button to select our previous database file name, Northwind.mdb. Yours may be at different location, adjust accordingly. Clear the User name: field.
Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3 | Part 4 | Part 5
