< C++ .NET System::IO - Files 5 | Main | C++ .NET System::IO - Files 7 >
Working with Files 6
What we have in this page?
8. Now that you know what sort of object you have and what options the user wants, you can print out the details. The first case will be the details for a single file.
// Process files if (bItsAFile) { Console::Write(fi->Name); if (bSize) Console::Write(L" {0}", (Object^)(fi->Length)); if (bDate) Console::Write(L" {0}", File::GetLastAccessTime(fi->ToString()).ToString()); if (bAtts) { FileAttributes fa = File::GetAttributes(fi->ToString()); Console::Write(L" ");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Normal) == FileAttributes::Normal) Console::Write(L"<normal>"); else { if ((fa & FileAttributes::Archive) == FileAttributes::Archive) Console::Write(L"a"); if ((fa & FileAttributes::Hidden) == FileAttributes::Hidden) Console::Write(L"h"); if ((fa & FileAttributes::System) == FileAttributes::System) Console::Write(L"s"); if ((fa & FileAttributes::ReadOnly) == FileAttributes::ReadOnly) Console::Write(L"r"); if ((fa & FileAttributes::Compressed) == FileAttributes::Compressed) Console::Write(L"z"); if ((fa & FileAttributes::Encrypted) == FileAttributes::Encrypted) Console::Write(L"e"); } } Console::WriteLine(); }
The program always echoes the file name and then displays other information based on the options required by the user. The Length property needs to be boxed before it can be printed using Write. You have to get the last access time by using one of the static methods of the File class, which takes the file path as an argument; the easiest way to get the path is to use the ToString method of FileInfo. If the user has requested attributes, use the GetAttributes static member of File to get a FileAttributes object, and then use the bitwise AND operator (&) to match it against the various permissions defined in FileAttributes. This code is checking only six attributes; it would be easy to extend it to check more. |
9. Build and run your program. The following is a sample output.
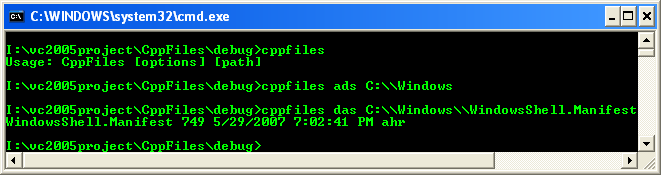
10. If the user has entered a directory path, list the contents of the directory. The following code lists subdirectories first and files second, and it lists directory names in uppercase and files in lowercase; you can obviously change this code to display these items however you prefer. Let’s start with the code for listing the subdirectories.
// Listing directory if it is directory
else if (bItsADirectory)
{
// List the directory contents - subdirectories first, then files
array<String^>^ dirs = Directory::GetDirectories(di->ToString());
for(int i=0; i<dirs->Length; i++)
{
DirectoryInfo^ sdi = gcnew DirectoryInfo(dirs->GetValue(i)->ToString());
// Directories list in upper case
String^ dirName = sdi->Name->ToUpper();
Console::Write(L"{0,30}",dirName);
// no size, so put a few blanks
String^ ss = L"—";
Console::Write(L"{0,12}", ss);
// last mod date is OK
if (bDate)
Console::Write(L" {0}", Directory::GetLastAccessTime(sdi->ToString()).ToString());
// no attributes, either
// finish the line
Console::WriteLine();
}
}

The Directory::GetDirectories function returns an array of strings representing the names of the subdirectories in the current directory. Because this is a .NET array, you can use the Length property to determine how many elements it has. For each array element, you create a DirectoryInfo object using the path name returned when ToString is called on the element.
The name is converted to uppercase and then printed out. Notice the use of a field width in the Write statement: format specifiers can take an optional field width after the field number. If this value is positive, the item is right justified in the field; if it’s negative, the item is left justified. A field width of 30 characters should be wide enough for most directory names. Directories don’t have a size, so output two hyphens as the size field. They do have a last access time, which can be obtained from the Directory class.
11. Build and run your program. Test by using a directory or file for the argument.

12. Process the file entries. This code follows the same pattern as that for the subdirectories but also includes some of the code from the single-file case:
// Now do the files
array<String^>^ files = Directory::GetFiles(di->ToString());
for(int i=0; i<files->Length; i++)
{
FileInfo^ fci = gcnew FileInfo(files->GetValue(i)->ToString());
// Files list in lower case
String^ fileName = fci->Name->ToLower();
Console::Write(L"{0, 30}", fileName);
if (bSize)
Console::Write(L"{0, 12}", (Object^)(fci->Length));
if (bDate)
Console::Write(L" {0}", File::GetLastAccessTime(fci->ToString()).ToString());
// Attributes
FileAttributes fa = File::GetAttributes(fi->ToString());
Console::Write(L" ");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Normal) == FileAttributes::Normal)
Console::Write(L"<normal>");
else
{
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Archive) == FileAttributes::Archive)
Console::Write(L"a");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Hidden) == FileAttributes::Hidden)
Console::Write(L"h");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::System) == FileAttributes::System)
Console::Write(L"s");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::ReadOnly) == FileAttributes::ReadOnly)
Console::Write(L"r");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Compressed) == FileAttributes::Compressed)
Console::Write(L"z");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Encrypted) == FileAttributes::Encrypted)
Console::Write(L"e");
}
// finish the line
Console::WriteLine();
}
The Directory::GetFiles static method returns an array of strings representing the files in the current directory. As before, you construct an object to represent each file and then query it. You do this exactly the same way as for the single-file case earlier in the exercise.
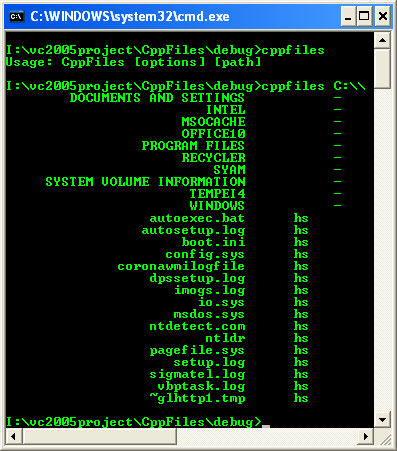
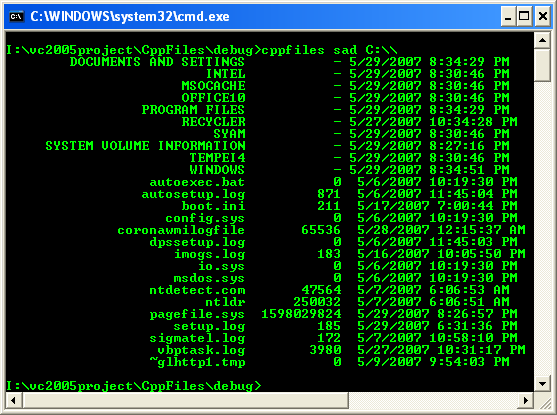
13. Build the application, open a console window and run the program with a suitable command line, such as the following:
Cppfiles C:\\ and Cppfiles sad C:\\WINDOWS etc.
You should see output similar to the following figure, which lists the files and directories.
 |
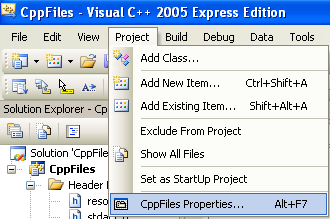
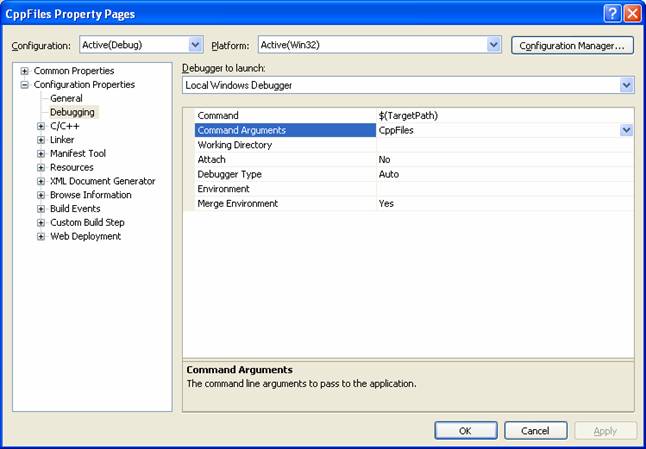
If you want to run the program under the Microsoft Visual Studio .NET debugger, you will need to provide the command-line arguments for the application. To do so, bring up the property pages for the project, select the Debugging option under Configuration Properties, and enter the arguments in the Command Arguments edit control. You can now run the program in debug mode.
A complete source code for this part is given below.
// CppFiles.cpp : main project file.
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace System;
using namespace System::IO;
int main()
{
// Get the command line arguments
array<String^>^args = Environment::GetCommandLineArgs();
// Check for required arguments
if (args->Length < 2)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"Usage: CppFiles [options] [path]");
return 0;
}
String^ options = nullptr;
String^ path = nullptr;
bool bGotOptions = false;
// Split out the arguments
if (args->Length == 3)
{
bGotOptions = true;
options = gcnew String(args[1]);
path = gcnew String(args[2]);
}
else if (args->Length == 2)
path = gcnew String(args[1]);
bool bSize = false;
bool bDate = false;
bool bAtts = false;
// If we have options, check them. The default is to list
// the name only
// Possible options are:
// v verbose listing, gives name, size & access time
// s list size
// d list last access date
// a list attributes
if (bGotOptions)
{
options = options->ToLower();
if (options->IndexOf('v') != -1)
{
bSize = true;
bDate = true;
bAtts = true;
}
else
{
if (options->IndexOf('s') != -1) bSize = true;
if (options->IndexOf('d') != -1) bDate = true;
if (options->IndexOf('a') != -1) bAtts = true;
}
}
// Check whether the user has entered a file or a directory
bool bItsAFile = false;
bool bItsADirectory = false;
FileInfo^ fi = gcnew FileInfo(path);
DirectoryInfo^ di = gcnew DirectoryInfo(path);
if (fi->Exists)
bItsAFile = true;
else if (di->Exists)
bItsADirectory = true;
if (!bItsAFile && !bItsADirectory)
{
Console::WriteLine(L"No such file or directory");
return(-1);
}
// Process files
if (bItsAFile)
{
Console::Write(fi->Name);
if (bSize)
Console::Write(L" {0}", (Object^)(fi->Length));
if (bDate)
Console::Write(L" {0}", File::GetLastAccessTime(fi->ToString()).ToString());
if (bAtts)
{
FileAttributes fa = File::GetAttributes(fi->ToString());
Console::Write(L" ");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Normal) == FileAttributes::Normal)
Console::Write(L"<normal>");
else
{
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Archive) == FileAttributes::Archive)
Console::Write(L"a");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Hidden) == FileAttributes::Hidden)
Console::Write(L"h");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::System) == FileAttributes::System)
Console::Write(L"s");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::ReadOnly) == FileAttributes::ReadOnly)
Console::Write(L"r");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Compressed) == FileAttributes::Compressed)
Console::Write(L"z");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Encrypted) == FileAttributes::Encrypted)
Console::Write(L"e");
}
}
Console::WriteLine();
}
// Listing directory if it is directory
else if (bItsADirectory)
{
// List the directory contents - subdirectories first, then files
array<String^>^ dirs = Directory::GetDirectories(di->ToString());
for(int i=0; i<dirs->Length; i++)
{
DirectoryInfo^ sdi = gcnew DirectoryInfo(dirs->GetValue(i)->ToString());
// Directories list in upper case
String^ dirName = sdi->Name->ToUpper();
Console::Write(L"{0,30}",dirName);
// no size, so put a few blanks
String^ ss = L"—";
Console::Write(L"{0,12}",ss);
// last mod date is OK
if (bDate)
Console::Write(L" {0}", Directory::GetLastAccessTime(sdi->ToString()).ToString());
// no attributes, either
// finish the line
Console::WriteLine();
}
}
// Now do the files
array<String^>^ files = Directory::GetFiles(di->ToString());
for(int i=0; i<files->Length; i++)
{
FileInfo^ fci = gcnew FileInfo(files->GetValue(i)->ToString());
// Files list in lower case
String^ fileName = fci->Name->ToLower();
Console::Write(L"{0, 30}", fileName);
if (bSize)
Console::Write(L"{0, 12}", (Object^)(fci->Length));
if (bDate)
Console::Write(L" {0}", File::GetLastAccessTime(fci->ToString()).ToString());
// Attributes
FileAttributes fa = File::GetAttributes(fi->ToString());
Console::Write(L" ");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Normal) == FileAttributes::Normal)
Console::Write(L"<normal>");
else
{
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Archive) == FileAttributes::Archive)
Console::Write(L"a");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Hidden) == FileAttributes::Hidden)
Console::Write(L"h");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::System) == FileAttributes::System)
Console::Write(L"s");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::ReadOnly) == FileAttributes::ReadOnly)
Console::Write(L"r");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Compressed) == FileAttributes::Compressed)
Console::Write(L"z");
if ((fa & FileAttributes::Encrypted) == FileAttributes::Encrypted)
Console::Write(L"e");
}
// finish the line
Console::WriteLine();
}
return 0;
}
Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3 | Part 4 | Part 5 | Part 6 | Part 7