< C++ .NET Operator Overloading 5 | Main | C++ .NET Operator Overloading 7 >
Operator Overloading 6
The CLS methods
Let take examples from the Decimal structure that used to represents a decimal number. The related overloaded operators (functions or methods as well) available as public methods of the Decimal structure members are: |
| Name | Description |
|
| |
| ... | … |
| op_Addition | Adds two specified Decimal values. |
| op_Decrement | Decrements the Decimal operand by one. |
| op_Division | Divides two specified Decimal values. |
| op_Equality | Returns a value indicating whether two instances of Decimal are equal. |
| op_Explicit | Overloaded. Converts the value of a Decimal object to another type. |
| op_GreaterThan | Returns a value indicating whether a specified Decimal is greater than another specified Decimal. |
| op_GreaterThanOrEqual | Returns a value indicating whether a specified Decimal is greater than or equal to another specified Decimal. |
| op_Implicit | Overloaded. Converts the value of a type to a Decimal value. |
| op_Increment | Increments the Decimal operand by 1. |
| op_Inequality | Returns a value indicating whether two instances of Decimal are not equal. |
| op_LessThan | Returns a value indicating whether a specified Decimal is less than another specified Decimal. |
| op_LessThanOrEqual | Returns a value indicating whether a specified Decimal is less than or equal to another specified Decimal. |
| op_Modulus | Returns the remainder resulting from dividing two specified Decimal values. |
| op_Multiply | Multiplies two specified Decimal values. |
| op_Subtraction | Subtracts two specified Decimal values. |
| op_UnaryNegation | Negates the value of the specified Decimal operand. |
| op_UnaryPlus | Returns the value of the Decimal operand (the sign of the operand is unchanged). |
| ... | … |
|
Table 4 | |
Decimal.op_Addition Method
| Item | Description |
| Method | Decimal.op_Addition |
| Purpose | Adds two specified Decimal values. |
| Namespace and assembly | Namespace: System Assembly: mscorlib (in mscorlib.dll) |
| Syntax | public: static Decimal operator + (Decimal d1, Decimal d2) |
| Parameters | d1 - A Decimal. d2 - A Decimal |
| Return value | The Decimal result of adding d1 and d2. |
| Example | - |
| Exceptions | OverflowException - the return value is less than MinValue or greater than MaxValue |
|
Table 5 | |
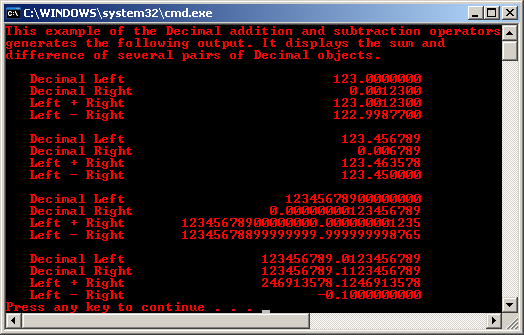
The following program example creates several pairs of Decimal values and calculates their sums with the Addition operator.
// operator.cpp : main project file.
// Example of the Decimal addition and subtraction operators.
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace System;
// Display Decimal parameters and their sum and difference.
void ShowDecimalSumDiff(Decimal Left, Decimal Right)
{
// Formatting the data for display
String^ dataFmt = " {0,-18}{1,31}";
Console::WriteLine();
Console::WriteLine(dataFmt, "Decimal Left", Left);
Console::WriteLine(dataFmt, "Decimal Right", Right);
Console::WriteLine(dataFmt, "Left + Right", Left + Right);
Console::WriteLine(dataFmt, "Left - Right", Left - Right);
}
int main(array<System::String ^> ^args)
{
Console::WriteLine("This example of the Decimal "
"addition and subtraction operators \ngenerates the "
"following output. It displays the sum and \n"
"difference of several pairs of Decimal objects.");
// Create pairs of Decimal objects.
ShowDecimalSumDiff(Decimal(1230000000, 0, 0, false, 7), Decimal::Parse("0.0012300"));
ShowDecimalSumDiff(Decimal::Parse("123.456789"), Decimal::Parse("0.006789"));
ShowDecimalSumDiff(Decimal::Parse("12345678900000000"), Decimal::Parse("0.00000000123456789"));
ShowDecimalSumDiff(Decimal::Parse("123456789.0123456789"), Decimal::Parse("123456789.1123456789"));
return 0;
}
Output:
Decimal.op_Decrement Method
| Item | Description |
| Method | Decimal.op_Decrement |
| Purpose | Decrements the Decimal operand by one. |
| Namespace and assembly | Namespace: System Assembly: mscorlib (in mscorlib.dll) |
| Syntax | public: static Decimal operator -- (Decimal d) |
| Parameters | d - The Decimal operand. |
| Return value | The value of d decremented by 1. |
| Example | - |
| Exceptions | OverflowException - the return value is less than MinValue or greater than MaxValue. |
|
Table 6 | |
The following program example applies the Decrement operator to several Decimal values.
// operator.cpp : main project file.
// Example of the Decimal increment, decrement, unary negation, and
// unary plus operators.
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace System;
// Get the exception type name; remove the namespace prefix.
String^ GetExceptionType(Exception^ ex)
{
String^ exceptionType = ex->GetType()->ToString();
return exceptionType->Substring( exceptionType->LastIndexOf('.') + 1);
}
// Display the argument and the incremented and decremented values.
void DecIncrDecrUnary(Decimal argument)
{
Decimal toBeIncr = argument;
Decimal toBeDecr = argument;
Console::WriteLine("{0,-26}{1}", "Decimal argument: ", argument);
// Catch the exception if the increment operator throws one.
Console::Write("{0,-26}", "argument ++");
try
{
toBeIncr++;
Console::WriteLine("{0}", toBeIncr);
}
catch (Exception^ ex)
{
Console::WriteLine("{0}", GetExceptionType(ex));
}
// Catch the exception if the decrement operator throws one.
Console::Write("{0,-26}", "argument --");
try
{
toBeDecr--;
Console::WriteLine("{0}", toBeDecr);
}
catch (Exception^ ex)
{
Console::WriteLine("{0}", GetExceptionType(ex));
}
Console::WriteLine();
}
int main(array<System::String ^> ^args)
{
Console::WriteLine("This example of the Decimal increment, "
"decrement, unary negation, \nand unary plus operators "
"generates the following output. It \ndisplays the "
"results of the operators on several Decimal values.\n");
// Create objects to compare with the reference.
DecIncrDecrUnary(Decimal::Parse("0.000000123"));
DecIncrDecrUnary(Decimal(123000000,0,0,false,9));
DecIncrDecrUnary( -Decimal(123000000,0,0,false,9));
DecIncrDecrUnary( +Decimal::MaxValue);
DecIncrDecrUnary( -Decimal::MaxValue );
DecIncrDecrUnary( +Decimal::Parse("7.5000000000000000000000000001"));
return 0;
}
Output:

Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3 | Part 4 | Part 5 | Part 6 | Part 7