< C++ .NET Exception Handling 5 | Main | C++ .NET Exception Handling 7 >
Exception Handling 6
What we have in this page?
safe_cast and Generic Types
The following sample shows that safe_cast can perform a downcast with a generic type.
|
safe_cast and User-Defined Conversions (UDC)
The following sample shows that user-defined conversions can be invoked by a safe_cast.
// mysafecast.cpp : main project file - safe_cast and
// user defined conversion, UDC
// compile with: /clr
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace System;
value struct myV;
ref struct myR
{
int x;
myR() { x = 1; }
myR(int argx) { x = argx; }
static operator myR::myV^(myR^ r);
};
value struct myV
{
int x;
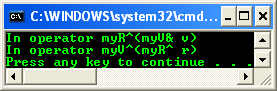
static operator myR^(myV& v)
{
Console::WriteLine("In operator myR^(myV& v)");
myR^ r = gcnew myR();
r->x = v.x;
return r;
}
myV(int argx) { x = argx; }
};
myR::operator myV^(myR^ r)
{
Console::WriteLine("In operator myV^(myR^ r)");
return gcnew myV(r->x);
}
int main(array<System::String ^> ^args)
{
bool fReturnVal = false;
myV v(2);
// should invoke UDC
myR^ r = safe_cast<myR^>(v);
// should invoke UDC
myV^ v2 = safe_cast<myV^>(r);
return 0;
}
Output:
safe_cast and Boxing
Boxing in defined as a compiler-injected, user-defined conversion. Therefore, safe_cast can be used to box a value on the CLR heap. The following sample shows boxing with simple and user defined value types. A safe_cast will box a value type variable that is on the native stack so it can be assigned to a variable on the garbage-collected heap. Try the following example by using the previous project.
// mysafecast.cpp : main project file - safe_cast and boxing.
// compile with: /clr
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace System;
interface struct myI {/* more code */};
value struct myV : public myI
{
int m_x;
myV(int i) : m_x(i) {/* more code */}
};
int main(array<System::String ^> ^args)
{
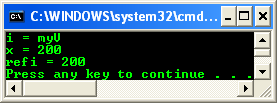
// box a value type
myV v(100);
// myV to myI
myI^ i = safe_cast<myI^>(v);
Console::WriteLine("i = {0}", i);
int x = 200;
myV^ refv = safe_cast<myV^>(v);
Console::WriteLine("x = {0}", x);
int^ refi = safe_cast<int^>(x);
Console::WriteLine("refi = {0}", refi);
return 0;
}
Output:
The following sample shows that boxing has a higher priority over a user-defined conversion in a safe_cast operation:
// mysafecast.cpp : main project file – another safe_cast and boxing
// compile with: /clr
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace System;
static bool fRetval = true;
interface struct myI {/* more code */};
value struct myV : public myI
{
int x;
myV(int argx)
{ x = argx; }
static operator myI^(myV v)
{
fRetval = false;
myI^ pi = v;
return pi;
}
};
ref struct myR
{
myR() {/* more code */}
myR(myV^ pv) {/* more code */}
};
int main(array<System::String ^> ^args)
{
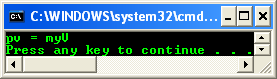
myV v(100);
// boxing will occur, not UDC "operator I^"
myI^ pv = safe_cast<myI^>(v);
Console::WriteLine("pv = {0}", pv);
return 0;
}
Output:
---------------------------------------------
safe_cast and Unboxing
Unboxing in defined as a compiler-injected, user-defined conversion. Therefore, safe_cast can be used to unbox a value on the CLR heap. Unboxing is a user-defined conversion, but unlike boxing, unboxing must be explicitly, which means it must be performed by a static_cast, C-style cast, or safe_cast; unboxing cannot be performed implicitly. For example:
// mysafecast.cpp : main project file - safe_cast unboxing
// compile with: /clr
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace System;
int main(array<System::String ^> ^args)
{
System::Object ^ obj = 100;
// object to int
int x = safe_cast<int>(obj);
Console::WriteLine("x = {0}", x);
return 0;
}
Output:
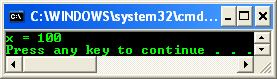
The following sample shows unboxing with value types and primitive types.
// mysafecast.cpp : main project file - safe_cast and unboxing
// compile with: /clr
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace System;
interface struct myI {};
value struct myVI : public myI {/* more code */};
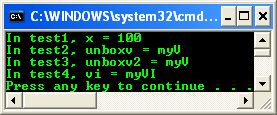
void test1() {
Object^ obj = 100;
int x = safe_cast<Int32>(obj);
Console::WriteLine("In test1, x = {0}", x);
}
value struct myV {
int x;
String^ sobj;
};
void test2() {
myV localv;
Object^ obj = localv;
myV unboxv = safe_cast<myV>(obj);
Console::WriteLine("In test2, unboxv = {0}", unboxv);
}
void test3() {
myV localv;
myV^ obj2 = localv;
myV unboxv2 = safe_cast<myV>(obj2);
Console::WriteLine("In test3, unboxv2 = {0}", unboxv2);
}
void test4() {
myI^ refi = myVI();
myVI vi = safe_cast<myVI>(refi);
Console::WriteLine("In test4, vi = {0}", vi);
}
int main(array<System::String ^> ^args)
{
test1();
test2();
test3();
test4();
return 0;
}
Output: