< .Net Type, Variable & Operator 7 | Main | .Net Type, Variable & Operator 9 >
Data Types, Variables and Operators 8
The discussion and the codes used supposed to be based on the new C++ .NET. The following is the topic in this part.
-
C++ .NET Types Program Examples
| C++ .NET Types Program Examples
The following examples demonstrate the use of .Net types in C++ .Net. Take note that the dot (.) in the .Net (used in VB .Net and C#) is replaced with the scope operator (::) in C++ .Net code. Create a new CLR Console Application project named Var and try all the program examples.
|
SByte (single byte) structure from System::SByte, represents an 8-bit signed integer. The following code example formats SByte values with several overloads of the ToString method.
// Var.cpp : main project file.
// Example for the SByte::ToString() methods.
// SByte structure, Single Byte represents an 8-bit signed integer
// This structure is not CLS-compliant...
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace System;
using namespace System::Globalization;
void RunToStringDemo()
{
SByte smallValue = -100;
SByte largeValue = 100;
// Format the Byte values without and with format strings.
Console::WriteLine("\nIFormatProvider is not used:");
Console::WriteLine(" {0,-20}{1,10}{2,10}", "No format string:", smallValue.ToString(), largeValue.ToString());
Console::WriteLine(" {0,-20}{1,10}{2,10}", "'X2' format string:", smallValue.ToString("X2"), largeValue.ToString("X2"));
// Get the NumberFormatInfo object from the invariant culture.
CultureInfo^ culture = gcnew CultureInfo("");
NumberFormatInfo^ numInfo = culture->NumberFormat;
// Set decimal digits to 0. Set the negative pattern to ( ).
numInfo->NumberDecimalDigits = 0;
numInfo->NumberNegativePattern = 0;
// Use the NumberFormatInfo object for an IFormatProvider.
Console::WriteLine("\nA NumberFormatInfo "
"object with negative pattern = ( ) and \nno "
"decimal digits is used for the IFormatProvider:");
Console::WriteLine(" {0,-20}{1,10}{2,10}", "No format string:", smallValue.ToString(numInfo), largeValue.ToString(numInfo));
Console::WriteLine(" {0,-20}{1,10}{2,10}", "'N' format string:", smallValue.ToString("N", numInfo), largeValue.ToString("N", numInfo));
}
int main(array<System::String ^> ^args)
{
Console::WriteLine("This example demonstrates:\n SByte::ToString(),\n"
" SByte::ToString(String*),\n"
" SByte::ToString(IFormatProvider*), and\n"
" SByte::ToString(String*, IFormatProvider*)\n"
"will generates the following output when formatting "
"SByte values \nwith combinations of format "
"strings and IFormatProvider.");
RunToStringDemo();
return 0;
}
Output:

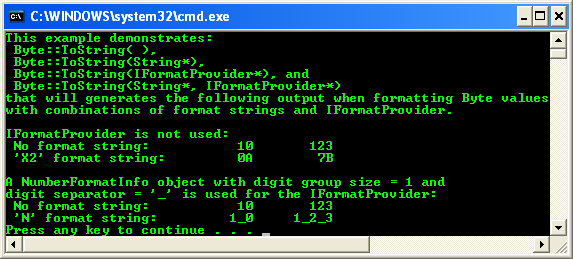
Byte structure from System::Byte represents an 8-bit unsigned integer. The following code example formats Byte values with several overloads of the ToString method.
// Var.cpp : main project file.
// Example for the Byte::ToString() methods.
// Byte structure represents an 8-bit unsigned integer
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace System;
using namespace System::Globalization;
void RunToStringDemo()
{
Byte smallValue = 10;
Byte largeValue = 123;
// Format the Byte values without and with format strings.
Console::WriteLine("\nIFormatProvider is not used:");
Console::WriteLine(" {0,-20}{1,10}{2,10}", "No format string:", smallValue.ToString(), largeValue.ToString());
Console::WriteLine(" {0,-20}{1,10}{2,10}", "'X2' format string:", smallValue.ToString("X2"), largeValue.ToString("X2"));
// Get the NumberFormatInfo object from the invariant culture.
CultureInfo^ culture = gcnew CultureInfo("");
NumberFormatInfo^ numInfo = culture->NumberFormat;
// Set the digit grouping to 1, set the digit separator
// to underscore, and set decimal digits to 0.
array<Int32>^sizes = {1};
numInfo->NumberGroupSizes = sizes;
numInfo->NumberGroupSeparator = "_";
numInfo->NumberDecimalDigits = 0;
// Use the NumberFormatInfo object for an IFormatProvider.
Console::WriteLine("\nA NumberFormatInfo object with digit group "
"size = 1 and \ndigit separator = '_' is used for the IFormatProvider:");
Console::WriteLine(" {0,-20}{1,10}{2,10}", "No format string:", smallValue.ToString(numInfo), largeValue.ToString(numInfo));
Console::WriteLine(" {0,-20}{1,10}{2,10}", "'N' format string:", smallValue.ToString("N", numInfo), largeValue.ToString("N", numInfo));
}
int main(array<System::String ^> ^args)
{
Console::WriteLine("This example demonstrates:\n Byte::ToString( ),\n"
" Byte::ToString(String*),\n"
" Byte::ToString(IFormatProvider*), and\n"
" Byte::ToString(String*, IFormatProvider*)\n"
"that will generates the following output when formatting "
"Byte values \nwith combinations of format "
"strings and IFormatProvider.");
RunToStringDemo();
return 0;
}
Output:
--------------------------------------------------------
Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3 | Part 4 | Part 5 | Part 6 | Part 7 | Part 8 | Part 9 | Part 10