< .Net Type, Variable & Operator 8 | Main | .Net Type, Variable & Operator 10 >
Data Types, Variables and Operators 9
The discussion and the codes used supposed to be based on the new C++ .NET. The following is the topic in this part.
-
C++ .NET Types Program Examples...continue
Double structure from System::Double, represents a double-precision floating point number. The following code example demonstrates generic and non-generic versions of the CompareTo method for Double and several other value and reference types.
// Var.cpp : main project file.
// CompareTo() method for several base types.
// The non-generic version takes a parameter of type Object, while the generic
// version takes a type-specific parameter, such as Boolean, Int32, or Double.
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace System;
void Show(String^ caption, Object^ var1, Object^ var2, int resultGeneric, int resultNonGeneric)
{
String^ relation;
Console::Write(caption);
if (resultGeneric == resultNonGeneric)
{
if (resultGeneric < 0)
relation = "less than";
else if (resultGeneric > 0)
relation = "greater than";
else
relation = "equal to";
Console::WriteLine("{0} is {1} {2}", var1, relation, var2);
}
// The following condition will never occur because the
// generic and non-generic CompareTo methods are equivalent.
else
{
Console::WriteLine("Generic CompareTo = {0}; non-generic CompareTo = {1}", resultGeneric, resultNonGeneric);
}
}
int main(array<System::String ^> ^args)
{
String^ nl = Environment::NewLine;
String^ msg = "{0}The following is the result of using the generic and non-generic{0}"
"versions of the CompareTo method for several base types:{0}";
// An Object used to insure CompareTo(Object) is called.
Object^ obj;
DateTime now = DateTime::Now;
// Time span = 11 days, 22 hours, 33 minutes, 44 seconds
TimeSpan tsX = TimeSpan(11,22,33,44);
// Version = 1.2.333.4
Version^ versX = gcnew Version("1.2.333.4");
// Guid = CA761232-ED42-11CE-BACD-00AA0057B223
Guid guidX = Guid("{CA761232-ED42-11CE-BACD-00AA0057B223}");
Boolean a1 = true,a2 = true;
Byte b1 = 1, b2 = 1;
Int16 c1 = -2, c2 = 2;
Int32 d1 = 3, d2 = 3;
Int64 e1 = 4, e2 = -4;
Decimal f1 = Decimal(-5.5), f2 = Decimal(5.5);
Single g1 = 6.6f, g2 = 6.6f;
Double h1 = 7.7, h2 = -7.7;
Char i1 = 'A', i2 = 'A';
String^ j1 = "abc", ^j2 = "abc";
DateTime k1 = now, k2 = now;
TimeSpan l1 = tsX, l2 = tsX;
Version^ m1 = versX, ^m2 = gcnew Version("2.0");
Guid n1 = guidX, n2 = guidX;
// The following types are not CLS-compliant.
SByte w1 = 8, w2 = 8;
UInt16 x1 = 9, x2 = 9;
UInt32 y1 = 10, y2 = 10;
UInt64 z1 = 11, z2 = 11;
// To standard output...
Console::WriteLine(msg, nl);
// Exception handling part...
try
{
// Show function call...
Show("Boolean: ", a1, a2, a1.CompareTo(a2), a1.CompareTo(a2));
Show("Byte: ", b1, b2, b1.CompareTo(b2), b1.CompareTo(b2));
Show("Int16: ", c1, c2, c1.CompareTo(c2), c1.CompareTo(c2));
Show("Int32: ", d1, d2, d1.CompareTo(d2), d1.CompareTo(d2));
Show("Int64: ", e1, e2, e1.CompareTo(e2), e1.CompareTo(e2));
Show("Decimal: ", f1, f2, f1.CompareTo(f2), f1.CompareTo(f2));
Show("Single: ", g1, g2, g1.CompareTo(g2), g1.CompareTo(g2));
Show("Double: ", h1, h2, h1.CompareTo(h2), h1.CompareTo(h2));
Show("Char: ", i1, i2, i1.CompareTo(i2), i1.CompareTo(i2));
// Use an anonymous object to hide the String object.
obj = j2;
Show("String: ", j1, j2, j1->CompareTo(j2), j1->CompareTo(obj));
Show("DateTime:", k1, k2, k1.CompareTo(k2), k1.CompareTo(k2));
Show("TimeSpan: ", l1, l2, l1.CompareTo(l2), l1.CompareTo(l2));
// Use an anonymous object to hide the Version object.
obj = m2;
Show("Version: ", m1, m2, m1->CompareTo(m2), m1->CompareTo(obj));
Show("Guid: ", n1, n2, n1.CompareTo(n2), n1.CompareTo(n2));
// Non-Common Language Specification compliant...
Console::WriteLine("{0}The following types are not CLS-compliant:", nl);
Show("SByte: ", w1, w2, w1.CompareTo(w2), w1.CompareTo(w2));
Show("UInt16: ", x1, x2, x1.CompareTo(x2), x1.CompareTo(x2));
Show("UInt32: ", y1, y2, y1.CompareTo(y2), y1.CompareTo(y2));
Show("UInt64: ", z1, z2, z1.CompareTo(z2), z1.CompareTo(z2));
}
catch (Exception^ e)
{ Console::WriteLine(e); }
return 0;
}
Output:

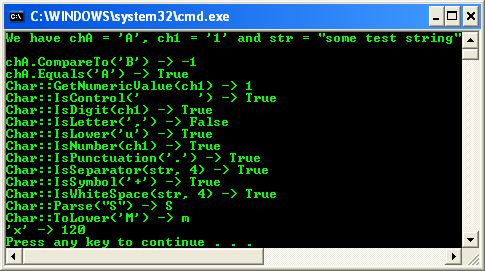
Char structure from System::Char represents a Unicode character. The following code example demonstrates some of the methods in Char.
// Var.cpp : main project file.
// Some of the methods available in Char program example
#include "stdafx.h"
using namespace System;
int main(array<System::String ^> ^args)
{
char chA = 'A';
char ch1 = '1';
String^ str = "some test string";
Console::WriteLine("We have chA = \'A\', ch1 = \'1\' and str = \"some test string\"");
Console::WriteLine();
// Output: "-1" (meaning 'A' is 1 less than 'B')
Console::WriteLine("chA.CompareTo(\'B\') -> {0}", chA.CompareTo('B'));
// Output: "True"
Console::WriteLine("chA.Equals(\'A\') -> {0}", chA.Equals('A'));
// Output: "1"
Console::WriteLine("Char::GetNumericValue(ch1) -> {0}", Char::GetNumericValue(ch1));
// Output: "True"
Console::WriteLine("Char::IsControl(\'\t\') -> {0}", Char::IsControl('\t'));
// Output: "True"
Console::WriteLine("Char::IsDigit(ch1) -> {0}", Char::IsDigit(ch1));
// Output: "False"
Console::WriteLine("Char::IsLetter(\',\') -> {0}", Char::IsLetter(','));
// Output: "True"
Console::WriteLine("Char::IsLower(\'u\') -> {0}", Char::IsLower('u'));
// Output: "True"
Console::WriteLine("Char::IsNumber(ch1) -> {0}", Char::IsNumber(ch1));
// Output: "True"
Console::WriteLine("Char::IsPunctuation(\'.\') -> {0}", Char::IsPunctuation('.'));
// Output: "True"
Console::WriteLine("Char::IsSeparator(str, 4) -> {0}", Char::IsSeparator(str, 4));
// Output: "True"
Console::WriteLine("Char::IsSymbol(\'+\') -> {0}", Char::IsSymbol('+'));
// Output: "True"
Console::WriteLine("Char::IsWhiteSpace(str, 4) -> {0}", Char::IsWhiteSpace(str, 4));
// Output: "S"
Console::WriteLine("Char::Parse(\"S\") -> {0}", Char::Parse("S"));
// Output: "m"
Console::WriteLine("Char::ToLower(\'M\') -> {0}", Char::ToLower('M'));
// Output: "x"
Console::WriteLine("\'x\' -> {0}", 'x');
return 0;
}
Output:
Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3 | Part 4 | Part 5 | Part 6 | Part 7 | Part 8 | Part 9 | Part 10